Definify.com
Definition 2026
前
前
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| | |||
Han character
前 (radical 18 刀+7, 9 strokes, cangjie input 廿月中弓 (TBLN), four-corner 80221, composition ⿱䒑刖)
Derived characters
References
- KangXi: page 140, character 15
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 2011
- Dae Jaweon: page 318, character 6
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 1, page 248, character 4
- Unihan data for U+524D
Chinese
|
simp. and trad. |
前 | |
|---|---|---|
| alt. forms | 歬 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 前
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Large seal script | Small seal script |
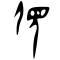 |
 |
 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (前) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 媊 | *ʔslel, *ʔslenʔ |
| 煎 | *ʔslen, *ʔslens |
| 湔 | *ʔslen, *ʔslens, *ʔsleːn, *zleːn |
| 鬋 | *ʔslen, *ʔslenʔ, *ʔslens |
| 剪 | *ʔslenʔ |
| 翦 | *ʔslenʔ |
| 譾 | *ʔslenʔ |
| 揃 | *ʔslenʔ |
| 箭 | *ʔslens |
| 葥 | *ʔslens |
| 前 | *zleːn |
| 騚 | *zleːn |
| 歬 | *zleːn |
Originally 歬, an ideogrammic compound (會意) : 止 (“foot”) + 舟 (“boat”) – a foot on a boat moving forward. Alternatively, 舟 represents a shoe (cf. Shuowen 履: 舟象履形) — a foot with a shoe on to walk forward. In the current form, 止 is simplified to 䒑 and 舟 to 月. The current form with an additional 刀 (“knife”) is the original form of 剪 (OC *ʔslenʔ, “to cut”).
Etymology 1
Pronunciation
- Mandarin
- Cantonese (Jyutping): cin4
- Hakka (Sixian, PFS): chhièn
- Min Nan (POJ): chêng / chiân / chûn
- Wu (Wiktionary): xxi (T3)
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄑㄧㄢˊ
- Wade-Giles: ch'ien2
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: chyan
- IPA (key): /t͡ɕʰi̯ɛn³⁵/
-

- (Standard Chinese, Beijing)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Jyutping: cin4
- Yale: chìhn
- Cantonese Pinyin: tsin4
- IPA (key): /t͡sʰiːn²¹/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou)+
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: chhièn
- Hakka Romanization System: qienˇ
- Hagfa Pinyim: qian2
- IPA: /t͡ɕʰi̯en¹¹/
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Min Nan
- (Hokkien)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: chêng / chiân / chûn
- Tâi-lô: tsîng / tsiân / tsûn
- Phofsit Daibuun: zeeng, cieen, zuun
- IPA (Xiamen): /t͡ɕiɪŋ²⁴/, /t͡ɕiɛn²⁴/, /t͡sun²⁴/
- IPA (Quanzhou): /t͡ɕiɪŋ²⁴/, /t͡ɕiɛn²⁴/, /t͡sun²⁴/
- IPA (Zhangzhou): /t͡ɕiɪŋ¹³/, /t͡ɕiɛn¹³/, /t͡sun¹³/
- IPA (Taipei): /t͡ɕiɪŋ²⁴/, /t͡ɕiɛn²⁴/, /t͡sun²⁴/
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /t͡ɕiɪŋ²³/, /t͡ɕiɛn²³/, /t͡sun²³/
- Note: chêng - vernacular; chiân - literary; chûn - borrowed.
- (Hokkien)
- Wu
- (Shanghainese)
- Wiktionary: xxi (T3)
- IPA (key): /ʑ̻i²³/
- (Shanghainese)
- Dialectal data▼
| Variety | Location | 前 |
|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Beijing | /t͡ɕʰian³⁵/ |
| Harbin |
/t͡ɕʰian²⁴/ ~天 /t͡ɕʰian²¹³/ 跟~兒 |
|
| Tianjin | /t͡ɕʰian⁴⁵/ | |
| Jinan | /t͡ɕʰiã⁴²/ | |
| Qingdao | /t͡sʰiã⁴²/ | |
| Zhengzhou | /t͡sʰian⁴²/ | |
| Xi'an | /t͡ɕʰiã²⁴/ | |
| Xining | /t͡ɕʰiã²⁴/ | |
| Yinchuan | /t͡ɕʰian⁵³/ | |
| Lanzhou | /t͡ɕʰiɛ̃n⁵³/ | |
| Ürümqi | /t͡ɕʰian⁵¹/ | |
| Wuhan | /t͡ɕʰiɛn²¹³/ | |
| Chengdu | /t͡ɕʰian³¹/ | |
| Guiyang | /t͡ɕʰian²¹/ | |
| Kunming | /t͡ɕʰiɛ̃³¹/ | |
| Nanjing | /t͡sʰien²⁴/ | |
| Hefei | /t͡ɕʰiĩ⁵⁵/ | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | /t͡ɕʰie¹¹/ |
| Pingyao |
/t͡ɕʰie̞¹³/ /t͡ɕie̞¹³/ |
|
| Hohhot | /t͡ɕʰie³¹/ | |
| Wu | Shanghai | /ʑi²³/ |
| Suzhou | /ziɪ¹³/ | |
| Hangzhou | /d͡ʑd͡ʑiẽ̞²¹³/ | |
| Wenzhou | /ji³¹/ | |
| Hui | Shexian | /t͡sʰe⁴⁴/ |
| Tunxi | /t͡sʰiɛ⁴⁴/ | |
| Xiang | Changsha | /t͡siẽ¹³/ |
| Xiangtan | /d͡ziẽ¹²/ | |
| Gan | Nanchang | /t͡ɕʰiɛn²⁴/ |
| Hakka | Meixian | /t͡sʰien¹¹/ |
| Taoyuan | /t͡sʰien¹¹/ | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | /t͡sʰin²¹/ |
| Nanning | /t͡sʰin²¹/ | |
| Hong Kong | /t͡sʰin²¹/ | |
| Min | Xiamen (Min Nan) |
/t͡sian³⁵/ /t͡siŋ³⁵/ |
| Fuzhou (Min Dong) | /t͡sieŋ⁵³/ | |
| Jian'ou (Min Bei) | /t͡sʰiŋ³³/ | |
| Shantou (Min Nan) | /t͡sõi⁵⁵/ | |
| Haikou (Min Nan) |
/sin³¹/ /tai³¹/ /tun³¹/ |
| Rime | |
|---|---|
| Character | 前 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Initial (聲) | 從 (15) |
| Final (韻) | 先 (85) |
| Tone (調) | Level (Ø) |
| Openness (開合) | Open |
| Division (等) | IV |
| Fanqie | 昨先切 |
| Reconstructions | |
| Zhengzhang Shangfang |
/d͡zen/ |
| Pan Wuyun |
/d͡zen/ |
| Shao Rongfen |
/d͡zɛn/ |
| Edwin Pulleyblank |
/d͡zɛn/ |
| Li Rong |
/d͡zen/ |
| Wang Li |
/d͡zien/ |
| Bernard Karlgren |
/d͡zʱien/ |
| Expected Mandarin Reflex |
qián |
| Baxter-Sagart system 1.1 (2014) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 前 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| Modern Beijing (Pinyin) |
qián |
| Middle Chinese |
‹ dzen › |
| Old Chinese |
/*[dz]ˤen/ (~ *m-dzˤen) |
| English | before |
Notes for Old Chinese notations in the Baxter-Sagart system: * Parentheses "()" indicate uncertain presence; | |
| Zhengzhang system (2003) | |
|---|---|
| Character | 前 |
| Reading # | 1/1 |
| No. | 10256 |
| Phonetic component |
前 |
| Rime group |
元 |
| Rime subdivision |
2 |
| Corresponding MC rime |
前 |
| Old Chinese |
/*zleːn/ |
Definitions
前
Compounds
|
|
|
Etymology 2
| For pronunciation and definitions of 前 – see 剪. (This character, 前, is an ancient form of 剪.) |
Japanese
Kanji
Readings
- Goon: ぜん (zen)
- Kan’on: せん (sen) (non-Jōyō reading)
- Kan’yōon: ぜ (ze) (non-Jōyō reading)
- Kun: まえ (mae), さき (saki) (non-Jōyō reading)
Compounds
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 前 |
|
まえ Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese as a compound of 目 (ma, “eye”) + 方 (he, “direction, -wards”).[1][2]
/mape/ > /maɸe/ > /mawe/ > /mae/
Pronunciation
Noun
前 (hiragana まえ, romaji mae, historical hiragana まへ)
Suffix
前 (hiragana まえ, romaji -mae)
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 前 |
|
さき Grade: 2 |
| kun'yomi |
From Old Japanese. Cognate with 崎 (saki, “a (geographical) point, where the land sticks out into the water”).[1]
Pronunciation
Noun
- Alternative spelling of 先 the tip of something; ahead, in front; before, earlier, the past; afterwards, the future; the destination of a motion or action
Usage notes
This sense is much more commonly spelled 先. See that entry for more details.
Etymology 3
From Middle Chinese 前 (dzen). Compare modern Mandarin 前 (qián).
Pronunciation
Counter
前 (hiragana ぜん, romaji -zen)
- counter for irregularly shaped objects such as desks, armrests, and serving trays
- counter for kami and shrines
Prefix
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 前 |
|
ぜ Grade: 2 |
| kan'yōon |
Contraction of 御前 (goze), itself a contraction of 御前 (gozen), an honorific form of address.[1][2]
Pronunciation
- Kan'yōyomi
- IPA(key): [ze̞]
Suffix
前 (hiragana ぜ, romaji -ze)
References
- 1 2 3 1988, 国語大辞典(新装版) (Kokugo Dai Jiten, Revised Edition) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan
- 1 2 3 4 5 2006, 大辞林 (Daijirin), Third Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13905-9
- 1 2 3 1998, NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 (NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary) (in Japanese), Tōkyō: NHK, ISBN 978-4-14-011112-3
- ↑ 1997, 新明解国語辞典 (Shin Meikai Kokugo Jiten), Fifth Edition (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Sanseidō, ISBN 4-385-13143-0